2025 - Thesis - Prototype
Neural_Diffusion, Sewing Patterns
Real-time is the only time. The rest is just latency. — Hash Firm Zurich
- If the hardware provides good enough memory bandwidth, then indexing becomes a more efficient / certain art than computing. Prompt some certain Numbers of different size for buildings + avoid lakes, etc. <- with
assigning some certain Hash Value for the diversityif you like, some Blender Demo Auto 3D Assets Prompting in Sep 2025. - In a non-uniform hash space, the physical distance between sampling points must be taken into account, otherwise the reconstruction will collapse. The drift term of backdiffusion must be scaled according to the metric tensor of the manifold.
spatial_dist = torch.norm(point_diff, dim=-1, keepdim=True) + 1e-8
normalized_diff = residual_diff / spatial_dist
Iter 1000–3000: HashSize ≈ full
Iter 4000–6000: HashSize ↓
Iter 7000+: HashSize << full # should be for Hash
Paper Generator™
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Problem Selection | Choose a widely used problem where optimality is rarely critical or empirically evaluated. |
| Hardness Injection | Force a reduction to a well-known NP-hard problem to establish theoretical difficulty. |
| Heuristic Recovery | Apply a textbook-level greedy or local search heuristic with minor variations. |
| Approximation Blessing | Provide a constant-factor approximation bound. Common values: 1/2, 1/e, 0.56 (“provable guarantee”). |
| Moral High Ground | Claim novelty through theoretical legitimacy rather than structural insight. |
Topic
- 2023 - AlphaDev discovers faster sorting algorithms
- 1993 - Computational Complexity - Christos Papadimitriou
-
2009 - Computational Complexity: A Modern Approach - Arora & Barak
- 2023 - Nuvo: Neural UV Mapping for Unruly 3D Representations
- 2021 - Shape As Points: A Differentiable Poisson Solver
- 2021 - Neural Geometric Level of Detail
- Tools in use, H200
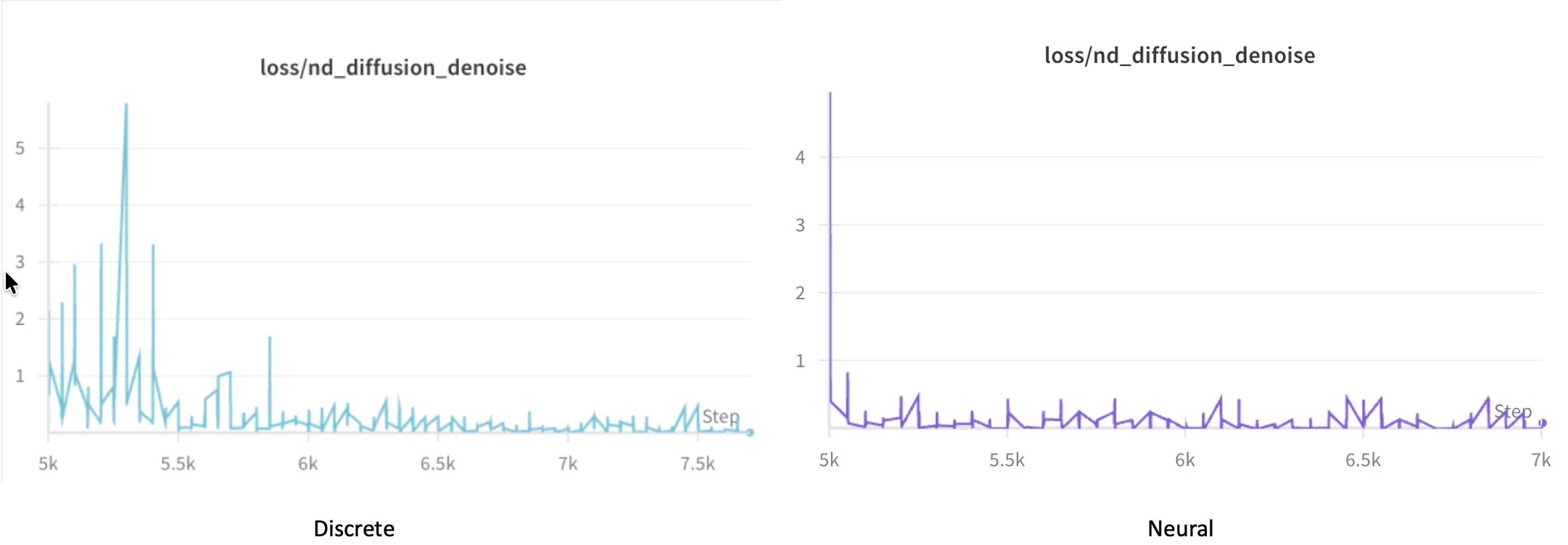
- Diffusion: 5 steps, beta=[0.0001, 0.02] <- [0.1, 0.8], Scaling residuals: std=1.2004 -> 0.1551
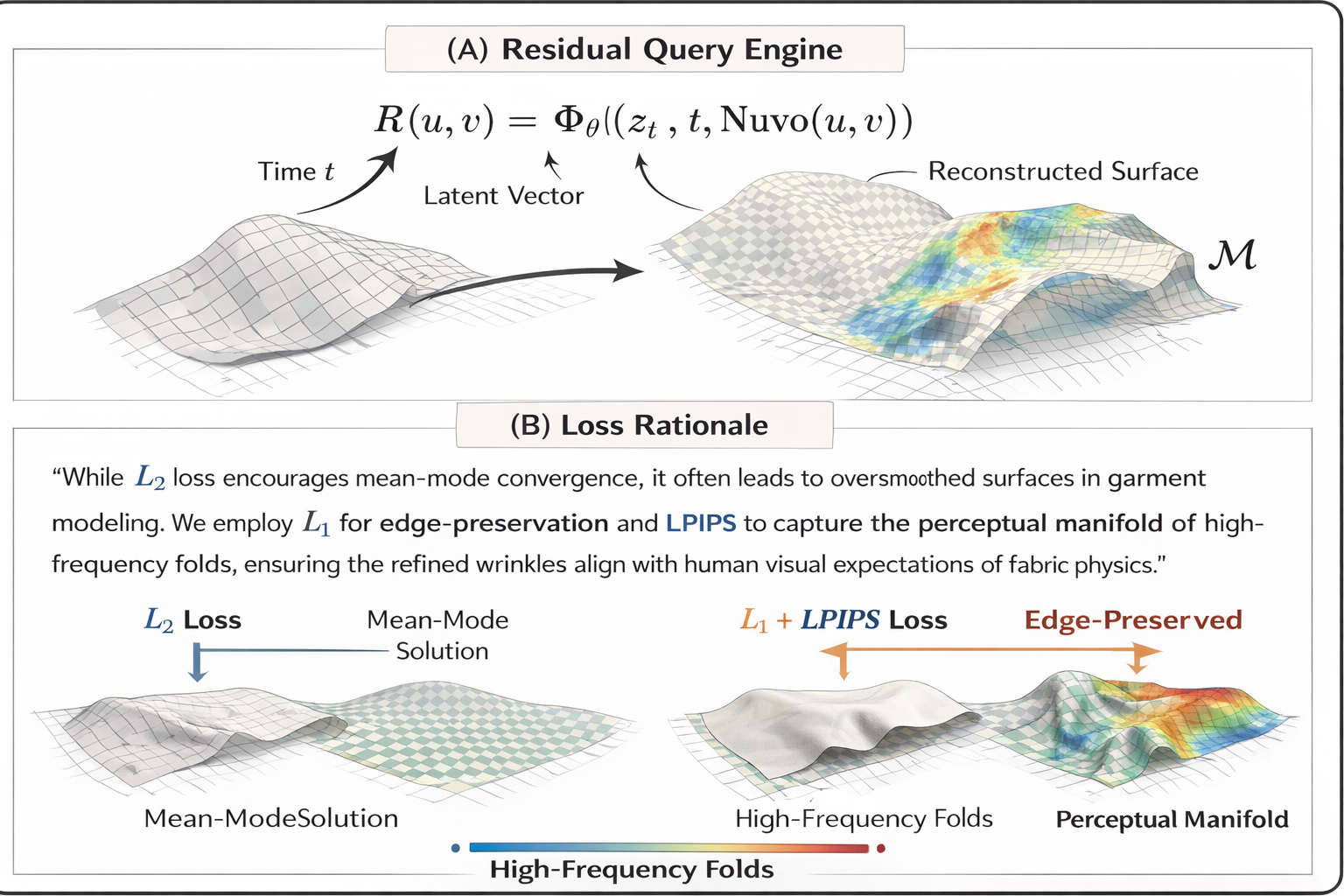
R(u,v) = Φ_θ((z_t, t, Nuvo(u,v)))
nuvo_features = diffusion_model.get_nuvo_features(points, nuvo_model)
spatial_dist = torch.norm(point_diff, dim=-1, keepdim=True) + 1e-8 <- change here for your 3D Hash value assignment
normalized_diff = residual_diff / spatial_dist <- change here
Config
- python train.py –config configs/icml.yaml –sample_idx 5 –material stiff –diffusion_steps 10
- **Stage 1** (0-5000): Nuvo only
- **Stage 2** (5000-10000): Nuvo + ND with hash assignment
num_iterations: 10000
diffusion_start_iter: 5000
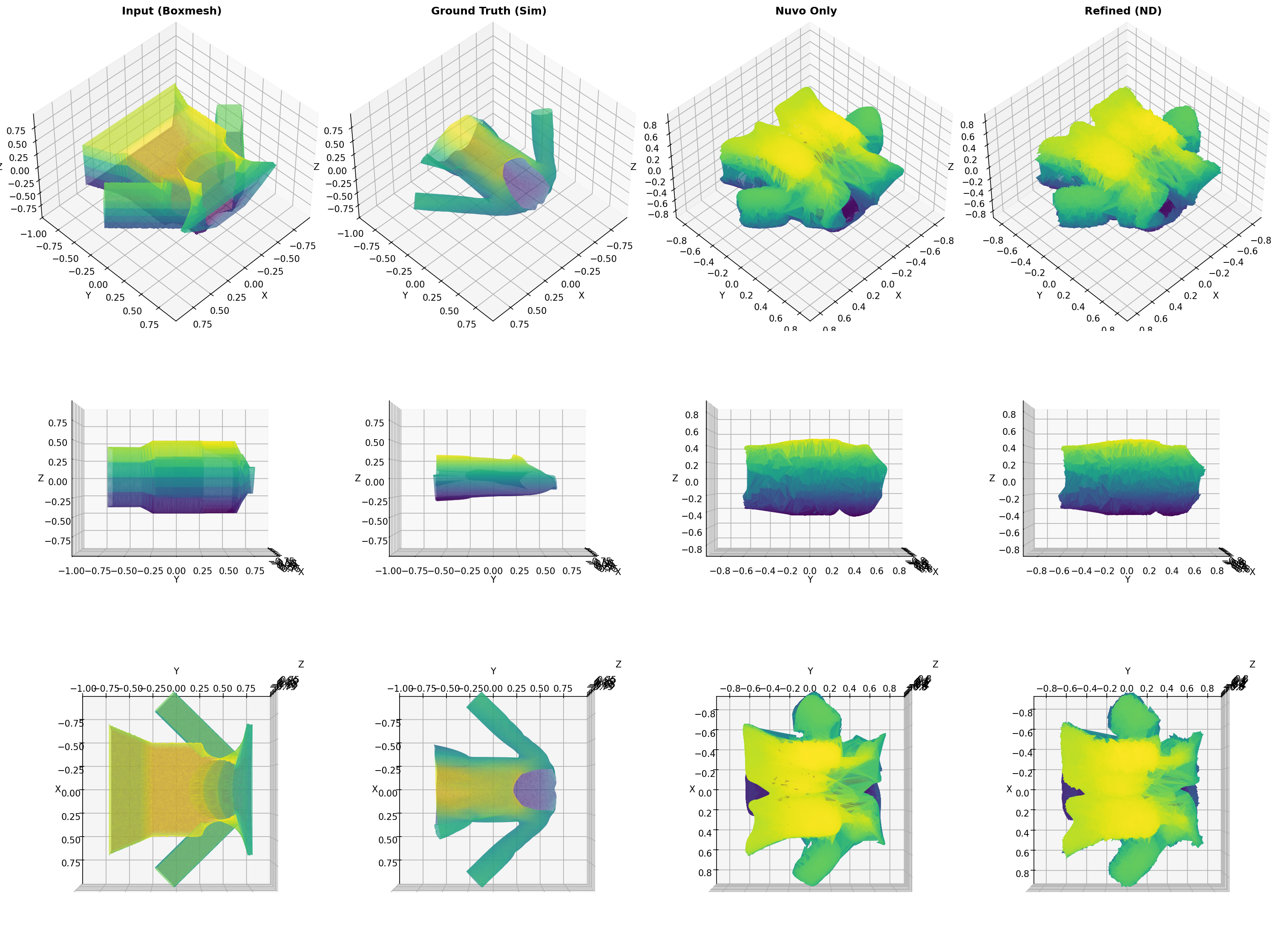
Input (Boxmesh) Details Analysis:
Vertices: 67970
Normal variation:
Mean: 0.076664
Std: 0.263265
Max: 2.000000
Curvature proxy:
Mean: 104265.058453
Std: 1197198.073828
Max: 92199800.035140
OK: Input (Boxmesh) has good details (mean >= 0.05)
Ground Truth (Sim) Details Analysis:
Vertices: 67970
Normal variation:
Mean: 0.443511
Std: 0.523963
Max: 1.999905
Curvature proxy:
Mean: 825298.086679
Std: 8333963.860213
Max: 196949800.860008
OK: Ground Truth (Sim) has good details (mean >= 0.05)
Residuals Analysis:
Mean magnitude: 0.222847
Std magnitude: 0.076963
Max magnitude: 0.530114
Min magnitude: 0.044882
OK: Residuals are significant (mean >= 0.05)
High-frequency residuals:
Mean: 0.087973
Max: 0.934507
OK: High-frequency details present
Tools
| Feature | Polyscope (Scientific Viewer) | Blender (Production Renderer) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary goal | Data inspection and debugging | High-fidelity visual rendering |
| Visual style | Flat shading; color-coded scalar fields (e.g., UV charts, normals, error maps) | Photorealistic materials; global illumination; ray tracing |
| Geometry support | Robust to raw meshes, point clouds, non-manifold geometry | Requires clean topology or high-poly meshes |
| Workflow | Immediate, programmatic (C++ / Python API) | Offline, manual setup (lights, cameras, shaders) |
| Role in paper | Qualitative analysis (UV consistency, error visualization) | Teaser and results (realistic wrinkles, shadows) |
End-to-End Dataflow
| Phase | Component | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Sewing pattern prior | SVG / JSON | 2D panel geometry, stitching graph, material constants |
| Base mesh $\mathcal{M}_{\text{base}}$ | OBJ / PLY | Coarse 3D garment surface (low-frequency folds) | |
| Anchor frame $x_{\text{anchor}}$ | Tensor | Initial shape distribution at $t_0$ | |
| Process | Nuvo mapping $f_\theta$ | MLP | Continuous mapping $(x,y,z)\rightarrow(u,v,k)$ over canonical UV charts |
| Reverse diffusion | ODE / SDE | 5–10 denoising steps in residual space $\mathcal{R}$ | |
| Loss constraints | Functions | $\mathcal{L}{\text{MSE}} + \mathcal{L}{\text{LPIPS}} + \mathcal{L}_{\text{L1}}$ | |
| Output | Residual field $R$ | Implicit / hash | High-frequency offsets (≤5% mesh scale) in UV space |
| Refined mesh $\mathcal{M}_{\text{ref}}$ | Mesh / points | $\mathcal{M}{\text{ref}}=\mathcal{M}{\text{base}}+R(u,v)$ | |
| Evaluation | Metrics | Scalars | Panel L2 (cm), stitch accuracy, perceptual fidelity (LPIPS) |
Overview
- We demonstrate that, under high-performance hardware (H200) conditions, constructing a geometry-aligned discrete hash field is the optimal solution for handling high-frequency garment details compared to stacking deep MLPs.
- By defining the diffusion process
within the residual hash space, we achieve 📍per-point refinement costdoes not scale with geometric complexity for complex nonlinear folds. -
three_two_three(bijective constraint): Equivalent toassert hash_map.size() == unique_points.size(). A low weight for this constraint indicates severe hash collisions, meaning multiple 3D points map to the same UV, resulting in a blurry rendering. -
cluster(clustering constraint): Equivalent toassert is_adjacent(p1, p2) == is_adjacent(hash(p1), hash(p2)). It ensures that spatially adjacent points are also close together in the hash bucket, preventing the rendering from becoming fragmented.
model:
num_charts: 8
use_vertex_duplication: true *https://github.com/ruiqixu37/Nuvo
-> then for the diffusion process -> It's just about tweaking details in a function space where the geometry is already aligned.
hidden_dim: 256
num_layers: 8
Assign Hash to your Nvidia sponsored renders
SELECT residual
FROM garment_surface
WHERE uv = (u, v);
- Nuvo is Data Indexer
- Diffusion is Error Corrector
- H200 is Hardware Accelerator
Can also add a “stitching graph consistency check”, which is essentially a Union-Find problem in graph theory, ensuring that the hash values at the stitching points of two pieces eventually converge to the same value.
- By discretize the 3D space:
- Hash function is Nuvo. It maps $P(x,y,z)$ to a specific (chart_id, u, v).
-
Keyis these UV coordinates. -
Valueis the corresponding geometric residual $R$. - The
beautylies in avoiding all the pitfalls of high-frequency signal fitting, because the hash table itself can perfectly store high-frequency information, requiringnoFourier transform patching. - In academia, this is called
Discrete Latent Space Alignment.
📍 Notes - Once it becomes discrete geometry, you don’t have to work on it anymore, all been solved by a large Hash Table -> let’s move on to Continuous Geometry / Signal Processing in Liver predictor
python train_demo.py --config configs/demo.yaml --sample_idx 5
Losses: Diffusion (MSE) + LPIPS
- diffusion_weight: 1.0
- lpips_weight: 0.5
- l1_weight: 0.5 (metric only)
Some Over-smooth Outcome
-
In LeetCode,
a coordinate pointis simply (x, y), the logic is very clear. However, in current computer graphics papers, the goal is to enable neural networks to optimize this point, The truth: This is essentially becauseMLPs (Neural Networks) are too inefficient / un-flexible, they can’t remember high-frequency details. So, people manually add “external storage” to them. -
In LeetCode, your opponent is computational complexity, at SIGGRAPH, your opponent is entropy.
- The hash-value mindset you
like(for example, Instant-NGP) is essentially a classic programmer’s counterattack. It no longer tries to understand complex geometric continuity. Instead, it says:I don’t care how complicated your surface is—I’ll just chop you up in hash space and look you up in a table - This approach—trading space for time, and lookup tables for computation—may have little aesthetic appeal in the eyes of mathematicians,
but on an H200, it runs the fastest
- The hash-value mindset you
Modern Hardware-aware Algorithm
- In the CPU era, algorithms aimed to reduce instruction cycles;
- In the GPU era, algorithms aim to achieve memory coalescing and avoid branch prediction.
The fundamental limitations of monocular (2D) video input
| Problem | Effect |
|---|---|
| Limited viewpoint | Depth, thickness, and surface normal directions are all ambiguous. |
| Lighting variation | Fur reflection, translucency, and self-occlusion make appearance unstable. |
| Strong deformation | Animal skin and fur exhibit local non-rigid motion. |
| No temporal supervision | Hard to maintain frame-to-frame consistency. |
Vector Field, Probability Flow, and the Continuity Equation in Diffusion / Flow
| Component | Mathematical Form | What It Represents | First Introduced / Formalized | Why It Was Introduced | Original Application Domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vector field | $u(x,t)$ | Local infinitesimal rule specifying how a state changes at position $x$ and time $t$ | Classical differential geometry (19th century); formalized in ODE theory | To describe continuous-time dynamical systems via local evolution rules | Mechanics, fluid dynamics |
| Probability density | $p(x,t)$ | Distribution of samples over state space at time $t$ | Laplace, Gauss (18th–19th century probability theory) | To describe uncertainty and population-level behavior | Statistical physics |
| Probability flow | $p(x,t),u(x,t)$ | Flux of probability mass through space | Boltzmann, Gibbs (late 19th century) | To model transport of mass or particles | Kinetic theory |
| Divergence operator | $\nabla\cdot(\cdot)$ | Net outflow vs inflow at a point | Gauss, Green (19th century analysis) | To quantify conservation laws | Electromagnetism, fluid flow |
| Continuity equation | $\displaystyle \frac{\partial p(x,t)}{\partial t} = -\nabla\cdot\big(p(x,t),u(x,t)\big)$ | Conservation law governing how probability density evolves | Liouville (1838); later generalized in physics | To enforce mass/probability conservation under dynamics | Hamiltonian systems, statistical mechanics |
| Interpretation in diffusion / flow | same equation | Distribution-level consequence of many samples following the same vector field | Adopted in modern form by Villani, Ambrosio; used in ML after 2019 | To connect sample dynamics with density evolution | Normalizing flows, diffusion models |
| Key conceptual role | — | Vector field generates the time evolution of the entire distribution | Mathematical fact, not a modeling choice | Enables continuous-time generative modeling | Flow models, continuous diffusion |
SUMO Bridge
┌────────────────────────────┐
│ SUMO Bridge (Traffic Sim) │
│ - Runs locally, offline │
│ - Outputs vehicle poses & │
│ event timestamps │
└─────────────┬──────────────┘
│
(Shared Memory / TCP localhost)
│
┌─────────────▼──────────────┐
│ Unreal Engine (VR Runtime) │
│ - Renders the scene │
│ - Receives SUMO data │
│ - Triggers audio events │
│ - Synchronizes pose with │
│ HTC Vive SDK │
└───────┬─────────┬──────────┘
│ │
(SteamVR API) (Audio EXE via DP port)
│ │
┌───────▼─────────▼──────────────┐
│ HTC Vive Headset + Controllers │
│ - IMU / Lighthouse tracking │
│ - Controller input via │
│ SteamVR runtime │
└────────────────────────────────┘
In a Hardware system, there are 3 essential layers
| Layer | Name | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Application Layer (App Layer) | Unreal / Unity / Blender / Games / Research Demos | Handles rendering, logic, and user interaction. |
| Runtime API Layer (Middleware) | OpenVR / OpenXR / Oculus SDK / WindowsMR | Provides VR hardware abstraction, pose tracking, frame synchronization, and display management. |
| Device Layer (Hardware Layer) | HTC Vive / Valve Index / Meta Quest / Varjo / Pimax | Represents the physical headset, controllers, and tracking sensors. |
User Feedback - If Dizzy
| Layer Frequency | Sensor / System | Primary Function | Role in Tracking Pipeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-frequency | IMU (gyroscope + accelerometer) | Real-time orientation estimation and pose prediction | Provides low-latency motion updates and enables motion-to-photon latency reduction |
| Mid-frequency | Photodiodes | Receive sweeping laser signals from base stations | Supplies angular constraints for pose correction |
| Low-frequency | Lighthouse base stations | Provide absolute spatial reference | Ensures global consistency and long-term drift correction |
| Fusion layer | Sensor fusion algorithms | Produce stable 6DoF pose estimates | Combines inertial prediction with optical correction into a coherent state estimate |
HTC Vive Tracking Architecture (Lighthouse System)
| Layer | Sensor / System | Function |
|---|---|---|
| High-frequency layer | IMU (gyroscope + accelerometer) | Real-time orientation estimation and pose prediction |
| Mid-frequency layer | Photodiodes | Receive sweeping laser signals |
| Low-frequency layer | Lighthouse base stations | Provide absolute spatial reference |
| Fusion layer | Sensor fusion algorithms | Produce stable 6DoF pose estimates |
HTC Vive Software Stack
| Layer | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Firmware | IMU sampling and hardware-level timestamping |
| Tracking runtime | Fusion of IMU and Lighthouse optical measurements |
| SteamVR | Provides 6DoF pose to the system |
| Application | Games and XR applications |
The Role of DP (DisplayPort)
| Component | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DP (DisplayPort) | Physical video interface | Transmits rendered frames from the GPU to the VR headset’s display. |
| Bandwidth | High data transfer rate | Supports dual-eye high-resolution output (e.g., 2K–4K per eye). |
| Refresh Rate | Frame delivery speed | Enables 90–120 Hz display updates to prevent motion sickness. |
| Latency | Image update timing | Ensures real-time synchronization between head movement and displayed image. |
| Relation to Runtime API | Software vs. hardware bridge | The Runtime API manages what is rendered; DisplayPort delivers it physically to the headset screen. |
Data Types
| Data Type | Direction | Example Content |
|---|---|---|
| Logical State Data | SUMO → Unreal | Vehicle position, velocity, and event timestamps |
| Rendering Commands / Image Frames | Unreal → Display Device (HMD) | Per-frame pixel buffers generated by the GPU |
| Pose / Interaction Data | Vive → Unreal | Controller and head IMU data, Lighthouse tracking signals |
| Audio Stream | Unreal → Audio Chip / DP / Audio EXE | PCM waveform data or triggered audio events |
Physical Layers For the Data Flow
1. SUMO ↔ Unreal Engine
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Transmission Type | Software-level communication (no physical cables) |
| Channel | Local inter-process communication (IPC) |
| Examples | TCP localhost, shared memory, Unix socket |
| Physical Layer | Data travels only inside the CPU main memory and system bus (PCIe), never leaving the host machine |
| Reason | SUMO and Unreal both run on the same PC. Shared memory or local sockets provide nanosecond-level latency without requiring physical network cables |
2. Unreal Engine ↔ HTC Vive (Headset + Controllers)
(1) Video and Audio Signals
| Type | Channel | Cable | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Video Frame Signal (Frame Buffer) | GPU → HMD Display | DisplayPort (DP) or HDMI | One-way (output) |
| Audio Stream (PCM / Compressed) | GPU / Motherboard → HMD Headphones | Audio sub-channel within DP or HDMI | One-way (output) |
(2) Sensor and Control Signals
| Type | Channel | Cable | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control Signals (USB HID) | Vive Headset ↔ PC | USB 3.0 Cable | Bidirectional |
| Controller Tracking (IMU, Lighthouse) | Vive Base Stations ↔ Headset ↔ PC | USB / Bluetooth / Wireless | Bidirectional |
Time Alignment
- Without an internet connection, there is no external time source (such as NTP or PTP). Therefore, all components must share a master clock, and every process synchronizes around it
- What happens if your master clock is the system clock
- You can run completely offline
- You can maintain full timestamp consistency between Unreal, the EXE, and the HMD as long as every process refers to the same local system time or the same bridge-provided clock derived from it
| Component | Role | Time Source | Works Offline? | Synchronization Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| System Clock | Hardware timer of OS | Physical wall time | Yes | Microsecond precision |
| Sync Server (C++) | Simulation scheduler | Derived from system clock | Yes | Defines frame order |
| SUMO Bridge | Produces simulation data | Receives time from Sync Server | Yes | Simulation step time |
| Unreal Engine | Renders VR scene | Driven by same time packets | Yes | Logical–physical mapping |
| HTC Vive / SteamVR | Device tracking | Uses same OS clock internally | Yes | Predictive frame timing |
| Audio EXE | Sound events | Reads sync timestamps via socket | Yes | Aligned playback timing |
┌────────────────────────┐
│ C++ SyncServer │ ← master process
│ - owns master clock │
│ - sends {frame_idx, t}│
└────────┬───────────────┘
│ sockets (localhost)
┌────────▼────────┐ ┌────────▼────────┐
│ Unreal Engine │ │ SUMO Process │
│ (Client) │ │ (Client) │
│ uses t, frame # │ │ uses t, frame # │
└─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
The essence of NTP
- To make sure that every computer (or process) in a network agrees on the same notion of time
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| NTP Server | Maintains accurate time (usually synchronized to GPS or atomic clock) |
| NTP Client | Periodically queries the server to adjust its local clock |
| Network Protocol | UDP (port 123), exchanging timestamps to compute delay and offset |
[ SUMO Process ]
│ Δt = 100 ms
▼
"SumoCommunicationRunnable"
│ sends {frame_id, sim_time}
▼
[ Local NTP / Sync Bridge ]
│ broadcasts {sim_time, delta}
▼
[ Unreal Engine Runtime ]
│
├── updates Actor transforms at t = sim_time
└── triggers AudioBridge event “engine_start” @ t = sim_time
│
▼
[ Audio EXE ]
aligns its playback clock to t = sim_time
Volumetric Representation vs. NeRF vs. Gaussian Splatting
| Property | Volumetric Representation | NeRF | Gaussian Splatting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Function form | Explicit voxel field $V(\mathbf{x})$ | Implicit neural field $f_{\theta}(\mathbf{x}, \mathbf{d})$ | Explicit Gaussian kernels ${G_i(\mathbf{x})}$ |
| Rendering | Numerical volume integration | Neural volume integration | Analytical Gaussian accumulation |
| Continuity | Piecewise (via interpolation) | Continuous (via MLP) | Continuous (via Gaussian kernel) |
| Optimization goal | Photometric consistency | Photometric consistency | Photometric consistency |
| Storage | Dense voxel grid | Network weights | Sparse Gaussian parameters |
| Computation | Heavy $\mathcal{O}(V^3)$ | Heavy $\mathcal{O}(R \times S)$ | Lightweight $\mathcal{O}(N)$ |
| Best suited for | Static volumetric scenes | High-quality static fields | Real-time dynamic 3D/4D scenes |
| Mathematical relation | Numerical approximation of volume integral | Neural approximation of the same integral | Analytical kernel approximation of the same integral |
Background Knowledge
- Reconstructing animatable 3D animal models — including mesh, appearance, and motion (pose, shape, texture) — directly from monocular videos of real animals, such as dogs.
- Unlike a typical “MLP-head over a backbone” architecture, this framework employs a template-based, parametric, and multi-modal reconstruction pipeline that combines mesh priors, implicit texture modeling, and dense geometric supervision.
Animal Avatars
| Contribution | Meaning | Relevance to Our Fur Layer |
|---|---|---|
| CSE + articulated mesh for dense supervision | Provides dense 2D-to-3D correspondences for every pixel, independent of viewpoint. | Our Gaussian fur geometry must be anchored to the mesh; this attachment relies on CSE. |
| Canonical + deformed duplex-mesh texture | Ensures semantic consistency and continuous appearance across poses. | Enables future extensions such as canonical fur color or reflectance fields. |
| Layered implicit field (inner and outer shells) | Represents texture within a volumetric region rather than a single surface. | Matches our volumetric Gaussian primitives, which naturally occupy a 3D volume. |
| Monocular reconstruction improved through CSE constraints | Provides strong supervision even for rear and side views. | Required for stable fur smoothness losses and future temporal constraints. |
Polynomial vs. Recursive Construction (Essential Differences for ML & Geometry)
| Aspect | Polynomial (Analytic / Global Form) | Recursive (de Casteljau / Local Form) |
|---|---|---|
| Influence of Control Points | Global — one control point affects the entire curve | Local — each segment depends only on nearby control points |
| Function Complexity | High-complexity global polynomial | Simple repeated linear interpolation |
| Learning Stability | Unstable (global coupling → noisy gradients) | Stable (local structure → smooth gradients) |
| Regularization | Weak — no inherent geometric constraints | Strong — recursive structure acts as built-in regularizer |
| Overfitting Risk | High | Low |
| Compatibility with ML | Poor for displacement or dynamic motion | Excellent for neural models (diffusion, deformation, 4D trajectories) |
| Extension to High Dimensions | Difficult (global interactions) | Easy (local updates generalize to 3D/4D motion) |
| Relation to Other Priors | — | Naturally compatible with B-Splines (local support) and natural parametrization (arc-length consistency) |
Trouble Shooting
- Your Ray
Camera parameters (R, T, intrinsics)
↓
Ray sampling → (x, y, z)
↓
Project to image plane (u, v)
↓
Sample RGB, mask, features at (u, v)
During Training
| Stage | Script File | Purpose / Function | Main Computation | Input | Output | GPU / CPU Usage | Typical Runtime |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Step 01 | main_preprocess_scene.py | Preprocessing – extract DensePose CSE embeddings and estimate PnP camera poses | Feature extraction and RANSAC-based camera pose estimation | Raw RGB frames + masks + metadata.sqlite | *_cse_predictions.pk, *_pnp_R_T.pk, visualization videos (.mp4) | Hybrid GPU + CPU • Detectron2 / DensePose → GPU • RANSAC → CPU | ≈ 30 min (202 frames on V100) |
| Step 02 | main_optimize_scene.py | Optimization – fit SMAL pose, shape, and texture parameters (+ fur layer) | Back-propagation + differentiable rendering + multi-loss optimization (Chamfer, CSE, Color, Laplacian, etc.) | Step 01 outputs (CSE + PnP) + init_pose + refined_mask | /experiments/<sequence>/ containing mesh/, texture/, log.txt, checkpoints/ | Mainly GPU • PyTorch3D + Lightplane + Triton kernels • CPU for I/O and data loading | 2 – 5 h (V100 32 GB) |
| Step 03 | main_visualize_reconstruction.py | Visualization – render and export 3D reconstruction results | Load mesh + texture → render turntable or overlay sequence | Experiment directory /experiments/<sequence>/ | Rendered video (.mp4) and final 3D models (.obj / .ply) | CPU + Light GPU (for rendering and encoding) | 3 – 10 min |
┌──────────────┐
│ CoP3D Video │
└──────┬───────┘
│ RGB + Mask + Metadata
▼
[Step 01] main_preprocess_scene.py
│
├─► CSE Embedding (.pk)
├─► Camera Extrinsics (.pk)
└─► Visualization (CSE / PnP .mp4)
▼
[Step 02] main_optimize_scene.py
│
├─► Optimize (SMAL Pose + Shape)
├─► Render Texture (Lightplane)
├─► Save Mesh / Texture / Logs
▼
[Step 03] main_visualize_reconstruction.py
└─► Rendered Demo Video (.mp4 / .obj)
During Training
| Stage / Parameter | Controlled Stage | Optimization Target / Scope | Related Module | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Shape Optimization (exp.n_shape_steps) | Geometry Stage | Optimizes mesh geometry, object pose, point cloud, or Gaussian primitive positions; may also refine camera extrinsics | SceneOptimizer.optimize_shape() | 1000–5000 |
Texture Optimization (exp.n_steps) | Texture Stage | Optimizes the texture MLP including color, lighting, reflectance, transparency, and shading parameters | SceneOptimizer.optimize_texture() | 1000–5000 |
Structure
| Component | Description | Key Idea / Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Parametric Template Model (SMAL) | Builds on SMAL, the animal counterpart of SMPL for humans. Serves as a template mesh prior with a consistent skeleton and deformation basis across sequences. | Provides structural consistency and controllable deformation for animatable 3D reconstruction. |
| Continuous Surface Embeddings (CSE) | Learns dense, continuous embeddings on the mesh surface instead of sparse keypoints. Enables image-to-mesh reprojection that aligns pixels to 3D points across views. | Offers view-agnostic supervision — embeddings remain stable and recognizable from any viewpoint, supporting robust multi-view and temporal consistency. |
| Implicit Duplex-Mesh Texture Model | Defines texture in a canonical pose, which deforms with pose and shape changes. Uses implicit texture fields for flexible, consistent appearance modeling. | Maintains realistic texture through deformations and ensures appearance consistency during rendering. |
| Per-Video Optimization Pipeline | Performs per-sequence fitting of shape, pose, texture, and embedding parameters, rather than training a general model. Implemented via main_optimize_scene.py. | Tailors reconstruction to each individual video, achieving high-fidelity, video-specific 3D models. |
| Overall Summary | Integrates parametric mesh priors, dense view-agnostic supervision, implicit texture fields, and per-video optimization into one pipeline. | Enables animatable, view-consistent 3D reconstruction from monocular videos. |
Step 02 – main_optimize_scene.py
| Stage | Component | Device (CPU/GPU) | Operation | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Load preprocessed data | get_input_cop_from_cfg() | CPU → GPU | Loads images, masks, cameras, CSE embeddings, etc., and transfers tensors to GPU. | Input comes from Step 01 outputs. |
| 2. Model initialization | initialize_pose_model() + initialize_texture_model() | GPU | Builds neural modules (pose, texture) and loads checkpoints if available. | Parameters moved to GPU memory. |
| 3. Differentiable rendering setup | PyTorch3D / Lightplane renderer | GPU | Prepares renderer with Cameras, Meshes, Textures for forward/backward passes. | Uses CUDA kernels and Triton ops. |
| 4. Optimization loop | SceneOptimizer.optimize_scene() | ✅ GPU (heavy) | Runs forward → loss → backward → update per epoch | Losses: Chamfer, CSE, Color, Laplace; gradients computed on GPU. |
| 5. Evaluation & checkpointing | CallbackEval, CallbackEarlyStop | GPU + CPU | Periodically evaluates PSNR, IoU and saves checkpoints. | Evaluation forward passes on GPU; logging on CPU. |
| 6. Rendering for inspection | vizrend.global_visualization() + viz.make_video_list() | GPU + CPU | Generates before/after videos of optimized scene. | GPU rasterization → CPU video encoding. |
Step 3 - main_visualize_reconstruction.py
| Stage | Component | Device (CPU/GPU) | Operation | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Load inputs | get_input_cop_from_archive() | CPU → GPU | Loads images, masks, cameras, embeddings, and moves tensors to the GPU | Uses .to(device) for tensors (e.g. images, masks, texture, cse_embedding) |
| 2. Load trained models | Inferencer.load_pose_model() + load_texture_model() | GPU | Loads checkpointed weights to pose_model and texture_model | Models are explicitly moved to GPU (.to(device)) |
| 3. Evaluation | CallbackEval.call() | GPU | Runs forward passes for test frames | Computes metrics like PSNR, IoU, LPIPS, etc. (all on GPU) |
| 4. Visualization (Rendering) | vizrend.global_visualization() | GPU + CPU | Performs differentiable rendering using PyTorch3D | Heavy GPU computation for mesh projection, rasterization, and lighting; CPU collects frames |
| 5. Video export | viz.make_video_list() | CPU | Concatenates rendered frames and encodes into MP4 | Uses ffmpeg or OpenCV on CPU; no training computation |
Readings
- 📍 2025 - TorchMesh: GPU-Accelerated Mesh Processing for Physical Simulation and Scientific Visualization in Any Dimension
- 2022 - GET3D: A Generative Model of High Quality 3D Textured Shapes Learned from Images
Python - If Can be A Dict Key
| Type | Can Be Dict Key | Hashable | Immutable | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
int | Yes | Yes | Yes | Numeric scalar |
float | Yes | Yes | Yes | Numeric scalar |
bool | Yes | Yes | Yes | Subclass of int |
str | Yes | Yes | Yes | Immutable text |
tuple | Yes* | Yes* | Yes | All elements must be hashable |
frozenset | Yes | Yes | Yes | Immutable set |
list | No | No | No | Mutable sequence |
set | No | No | No | Mutable set |
dict | No | No | No | Mutable mapping |
| Custom object (default) | Yes | Yes | Usually | Hash based on object identity |
Implicit vs Explicit Representations
| Concept | Implicit Representation | Explicit Representation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Geometry is represented by a continuous function (e.g., NeRF, SDF) that implicitly defines occupancy, density, or color at any 3D location. | Geometry is represented by explicit surface elements, such as vertices, faces, and normals in a mesh. |
| Typical Form | ( f_\theta(x, t) \rightarrow {\sigma, c} ) — density and color fields | ( (V, F) ) — mesh vertices and faces, deformed by pose parameters |
| Key Property | Continuous, topology-free, differentiable | Discrete, topology-fixed, physically interpretable |
| Advantages | ① Unconstrained topology ② Smooth and differentiable ③ Naturally fits neural fields | ① Precise control over surface ② Compatible with animation and rendering ③ Supports texture mapping and fur direction |
| Drawbacks | ① Ambiguous topology ② Hard to extract exact normals ③ Computationally heavy for rendering | ① Limited to known topology (e.g., SMAL) ② Difficult to generalize across species |
| Example | BANMo – implicit volumetric field + neural blend skinning | Animal Avatars – explicit SMAL mesh + CSE pixel alignment |
Geometric Shape Modeling
- 📍 2025 - TetWeave: Isosurface Extraction using On-The-Fly Delaunay Tetrahedral Grids for Gradient-Based Mesh Optimization - Multi-view 3d reconstruction, geometric texture generation, gradient-based mesh optimization, Isosurface Representation, 📍 Fabricaible
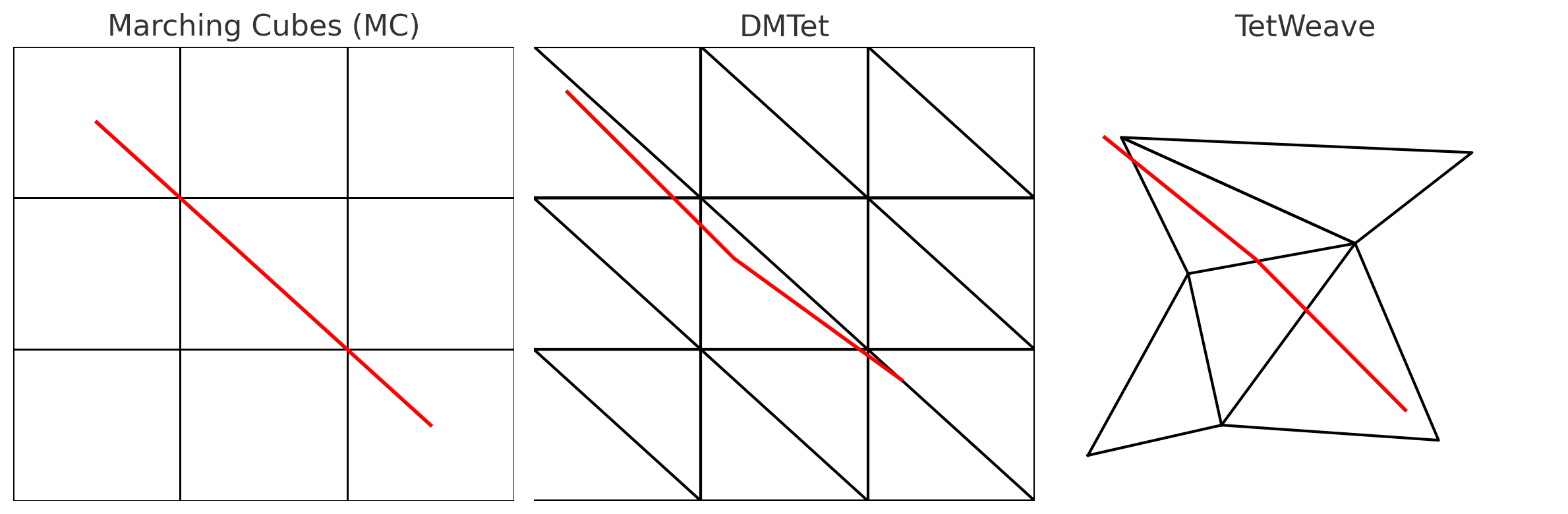
Marching Tetrahedra on Delaunay Triangulation
(isosurface extraction on arbitrary point clouds)
↓
Directional Signed Distance
(spherical harmonics; edge-aware surface accuracy)
↓
Adaptive Tetrahedral Grid
(resampling where error is high; grid fits unknown surfaces)
↓
Regularization Terms
(fairness + ODT loss; improve mesh quality, avoid slivers)
Mesh Generations
📍 2025 - VertexRegen: Mesh Generation with Continuous Level of Detail
- Controllable, ready-to-use mesh generation
- Use a
Coarse Meshto estimate the global resolution initially, then gradually refine it to the local resolution
1996 - Microsoft Research - Progressive Meshes
- Training data: Use edge collapse to compress the high-precision mesh into different levels
- Generation process: Use a generative model to learn the inverse operation—vertex splitting
- Thus, generation proceeds from coarse to fine, yielding a complete mesh at each step
2011 - High-quality passive facial performance capture using anchor frames
| Year | Paper | Type | Description | Core Mathematical Field |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025 | TetWeave: Isosurface Extraction using On-The-Fly Delaunay Tetrahedral Grids for Gradient-Based Mesh Optimization | 🧱 + ⚙️ Hybrid | Simultaneous mesh generation and optimization via differentiable Delaunay grids. | Computational Geometry + Variational Optimization |
| 2025 | Reconfigurable Hinged Kirigami Tessellations | 🧱 Mesh Generation | Generates deployable curved surfaces through geometric cutting and kinematic tiling. | Discrete Differential Geometry |
| 2025 | Computational Modeling of Gothic Microarchitecture | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Topological and shape optimization of architectural microstructures. | Topology Optimization |
| 2025 | Higher Order Continuity for Smooth As-Rigid-As-Possible Shape Modeling | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Extends ARAP formulation with higher-order geometric continuity. | Differential Geometry + PDE Optimization |
| 2024 | Mesh Parameterization Meets Intrinsic Triangulations | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Improves mesh parameterization and smoothness via intrinsic metrics. | Riemannian Geometry + Discrete Optimization |
| 2024 | Fabric Tessellation: Realizing Freeform Surfaces by Smocking | 🧱 Mesh Generation | Generates freeform surfaces via geometric fabric tessellation design. | Geometric Modeling + Computational Topology |
| 2024 | SENS: Part-Aware Sketch-based Implicit Neural Shape Modeling | 🧱 Mesh Generation | Generates 3D meshes from sketches using implicit neural fields. | Implicit Geometry + Neural Representation Learning |
| 2022 | Dev2PQ: Planar Quadrilateral Strip Remeshing of Developable Surfaces | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Remeshes curved surfaces into planar quadrilateral strips under developability constraints. | Differential Geometry + Discrete Optimization |
| 2022 | Iso-Points: Optimizing Neural Implicit Surfaces with Hybrid Representations | ⚗️ Hybrid | Optimizes implicit fields into explicit renderable meshes. | Differentiable Geometry + Variational Optimization |
| 2021 | Developable Approximation via Gauss Image Thinning | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Approximates surfaces toward developability constraints. | Differential Geometry + Optimization |
| 2020 | Properties of Laplace Operators for Tetrahedral Meshes | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Studies spectral and geometric properties of Laplace operators in tetrahedral meshes. | Spectral Geometry + Linear Algebra |
| 2015 | Instant Field-Aligned Meshes | 🧱 Mesh Generation | Generates meshes aligned with direction fields in real time. | Vector Field Theory + Discrete Geometry |
| 2014 | Pattern-Based Quadrangulation for N-Sided Patches | 🧱 Mesh Generation | Creates quadrilateral meshes using pattern-based surface decomposition. | Combinatorial Geometry + Topology |
| 2013 | Sketch-Based Generation and Editing of Quad Meshes | 🧱 Mesh Generation | Produces and edits quad meshes directly from sketch input. | Geometric Modeling + Computational Geometry |
| 2013 | Consistent Volumetric Discretizations Inside Self-Intersecting Surfaces | 🧱 Mesh Generation | Constructs consistent volumetric meshes inside complex self-intersecting surfaces. | Numerical Geometry + Discretization Theory |
| 2013 | Locally Injective Mappings | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Optimizes parameterizations to avoid fold-overs and self-intersections. | Nonlinear Optimization + Differential Geometry |
| 2007 | As-Rigid-As-Possible Surface Modeling (ARAP) | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Foundational method for geometric shape deformation and energy minimization. | Variational Optimization + Linear Algebra |
| 2006 | Laplacian Mesh Optimization | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Classical Laplacian-based geometric smoothing and reconstruction. | Discrete Differential Geometry + Linear Systems |
| 2004 | Laplacian Surface Editing | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Seminal differentiable deformation method for surface editing. | Variational Calculus + Linear Algebra |
| 2003 | High-Pass Quantization for Mesh Encoding | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Optimizes geometric compression via high-pass component quantization. | Signal Processing on Manifolds |
| 2002 | Bounded-Distortion Piecewise Mesh Parameterization | ⚙️ Mesh Optimization | Minimizes distortion under bounded mapping constraints. | Conformal Geometry + Convex Optimization |
References
- 2025 - TetWeave: Isosurface Extraction using On-The-Fly Delaunay Tetrahedral Grids
- 2024 - SENS: Part-Aware Sketch-Based Implicit Neural Shape Modeling
- 2022 - Enhancing computational fluid dynamics with machine learning
- 2025 - GLIMPSE: Generalized Locality for Scalable and Robust CT
- 2024 - WaveBench: Benchmarking Data-driven Solvers for Linear Wave Propagation PDEs
Fur
- 2024 - Controllable Neural Style Transfer for Dynamic Meshes
- 2025 - Shaping Strands with Neural Style Transfer
[1/3] ARAP / Laplacian-Based Surface Modeling Backbone (2004–2007)
| Year | Paper | Venue | Key Contribution | Backbone Significance | Relation to Neural Diffusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | Laplacian Surface Editing (Sorkine et al.) | SIGGRAPH | Introduced Laplacian coordinates for intuitive surface deformation | First practical formulation of surface refinement as energy minimization | Defines refinement as deterministic optimization (single solution) |
| 2005 | Surface Modeling with Laplacian-Based Operators | Eurographics | Unified Laplacian operators for smoothing and editing | Formalized discrete differential operators for surfaces | Fixed linear operators vs. learnable stochastic dynamics |
| 2007 | As-Rigid-As-Possible Surface Modeling (Sorkine & Alexa) | SIGGRAPH | ARAP energy preserves local rigidity under deformation | Canonical non-rigid surface refinement model | Neural Diffusion generalizes rigidity to probabilistic deformation |
| 2007 | Differential Coordinates for Interactive Mesh Editing | SIGGRAPH | Differential coordinates for local-global optimization | Established local-global iteration as refinement paradigm | Neural Diffusion replaces iterative optimization with continuous dynamics |
[2/3] Garment Simulation / Cloth Modeling Backbone (2002–2015)
| Year | Paper | Venue | Key Contribution | Backbone Significance | Relation to Neural Diffusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | Large Steps in Cloth Simulation (Baraff & Witkin) | SIGGRAPH | Implicit integration for stable cloth simulation | Foundation of modern cloth solvers | Deterministic physics vs. learned stochastic refinement |
| 2003 | Simulation of Clothing with Folds and Wrinkles | SIGGRAPH | Introduced realistic wrinkle formation | High-frequency surface detail modeling | Diffusion learns multi-scale detail without explicit physics |
| 2006 | Adaptive Cloth Simulation | SIGGRAPH | Efficient multi-resolution cloth modeling | Scale-aware surface refinement | Neural Diffusion offers continuous scale refinement |
| 2009 | Continuum-Based Strain Limiting for Cloth Simulation | SIGGRAPH | Strain limiting for stability | Constraint-based deformation | Constraints replaced by learned probabilistic priors |
| 2012 | A Multi-Scale Approach to Cloth Simulation (Narain et al.) | SIGGRAPH | Hierarchical refinement of cloth surfaces | Explicit multi-scale refinement | Diffusion learns refinement across scales automatically |
| 2015 | Position-Based Simulation Methods | SIGGRAPH Courses | Unified constraint-based deformable simulation | Widely adopted garment backbone | Neural Diffusion removes hand-designed constraint scheduling |
[3/3] Mesh-Based Surface Editing & Geometry Processing Backbone (2004–2012)
| Year | Paper | Venue | Key Contribution | Backbone Significance | Relation to Neural Diffusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2004 | Laplacian Surface Editing (Botsch et al.) | SIGGRAPH | Editing via sparse constraints | Made surface refinement interactive | Diffusion replaces hard constraints with learned distributions |
| 2006 | An Introduction to Mesh Processing | SIGGRAPH Course | Unified geometry processing framework | Codified mesh processing canon | Neural Diffusion introduces probabilistic processing |
| 2008 | On Linear Variational Surface Deformation Methods (Botsch & Sorkine) | IEEE TVCG | Analysis of linear deformation models | Theoretical grounding of refinement energies | Diffusion replaces linear energies with learned vector fields |
| 2010 | Polygon Mesh Processing (Book) | AK Peters | Comprehensive mesh processing reference | De facto geometry backbone | Neural Diffusion reframes mesh processing as distribution modeling |
| 2012 | Shape Deformation Using Moving Least Squares | SIGGRAPH | Smooth deformation without remeshing | Alternative refinement paradigm | Diffusion generalizes deformation to stochastic evolution |
Interface and Protocols
| Type | Full Name | Description | Example Tools / Interfaces | Typical Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GUI | Graphical User Interface | A visual, interactive interface that allows users to operate software through windows, buttons, and icons. Ideal for user-friendly, visual workflows. | Web browsers (Chrome, Safari), Cisco AnyConnect, LeoMed OnDemand, Finder / File Explorer | Click-based interaction, dashboards, visualization, web apps |
| CLI | Command-Line Interface | A text-based interface where users type commands to interact with the system. Enables direct control, scripting, and automation. | Terminal, zsh/bash shell, Linux shell, Windows PowerShell | Execute commands (ssh, scp, conda, git), automate tasks |
| SSH | Secure Shell Protocol | A secure network protocol for remote login, command execution, and encrypted data transfer. | ssh, PuTTY, OpenSSH client | Remote access, file transfer (scp, rsync), port forwarding |
| SFTP | Secure File Transfer Protocol | A file transfer protocol that works over SSH to securely upload or download files. | FileZilla, sftp, Cyberduck | Move datasets or logs between your computer and a remote server |
| RDP | Remote Desktop Protocol | Allows users to access a remote computer’s desktop GUI environment over a network. | Windows Remote Desktop, xRDP, LeoMed OnDemand (web GUI) | Open remote desktops, run GUI-based software remotely |
| HTTP/HTTPS | HyperText Transfer Protocol (Secure) | The standard protocol for web communication; HTTPS adds encryption for security. | Web browsers, REST APIs, Jupyter Notebook via browser | Access web services, APIs, dashboards, notebooks |
| VPN | Virtual Private Network | Creates a secure, encrypted connection (tunnel) between your device and a private network (e.g., ETH internal). | Cisco AnyConnect, OpenConnect | Access internal servers (e.g., leomed.ethz.ch, euler.ethz.ch) securely |
| VNC | Virtual Network Computing | A remote desktop sharing protocol independent of platform or OS. | RealVNC, TigerVNC, x11vnc | Access GUI sessions from macOS/Linux to remote HPC desktops |
| X11 / X-Forwarding | X Window System (Version 11) | A protocol that allows GUI applications running on a remote server to display on your local machine. | ssh -Y, XQuartz (macOS), MobaXterm (Windows) | Run GUI apps like MATLAB or visualization tools from servers |
| FTP / FTPS | File Transfer Protocol / Secure | A classic file transfer protocol; FTPS adds SSL/TLS encryption. | WinSCP, FileZilla, ftp command | Transfer files (less secure than SFTP; used in legacy systems) |
| API / REST API | Application Programming Interface | A structured interface that allows software components or servers to communicate via HTTP requests (often JSON-based). | curl, Postman, Python requests library | Access remote datasets, trigger jobs, or fetch information programmatically |
Historical Origins of Classical and Quantum Statistical Distributions
| Distribution | Proposed By | Year | Historical Context | Original Motivation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maxwell–Boltzmann | James Clerk Maxwell (1860), Ludwig Boltzmann (1872) | 1860–1872 | Classical thermodynamics and kinetic theory of gases during the Industrial Revolution | To explain macroscopic thermodynamic laws (pressure, temperature) from microscopic particle motion under classical mechanics assumptions |
| Fermi–Dirac | Enrico Fermi (1926), Paul Dirac (1926) | 1926 | Emergence of quantum mechanics and the discovery of the Pauli exclusion principle | To model the statistical behavior of indistinguishable fermions obeying quantum exclusion, especially electrons in atoms and solids |
| Bose–Einstein | Satyendra Nath Bose (1924), Albert Einstein (1924–1925) | 1924–1925 | Early quantum theory and photon statistics | To explain black-body radiation and collective quantum behavior of bosons, allowing multiple particles to occupy the same state |
References / Reading List - Shape Modeling
- Polyscope - Toolkit for demos
- SIGGRAPH 2025
- 2024 - DMesh: A Differentiable Mesh Representation
- 2025 - Piecewise Ruled Approximation for Freeform Mesh Surfaces
- 2025 - NeuralSVG: An Implicit Representation for Text-to-Vector Generation - logo Gen
- Toolkit - 2025 - Brainchop: In-browser 3D MRI rendering and segmentation
- 2025 - E-M3RF: An Equivariant Multimodal 3D Re-assembly Framework
- 2018 - End-to-end recovery of human shape and pose
2025
- 2025 - Single-Image 3D Human Reconstruction with 3D-Aware Diffusion Priors and Facial Enhancement
- 2025 - Find Any Part in 3D
- 2025 - Jamais Vu: Exposing the Generalization Gap in Supervised Semantic Correspondence
- 2024 - DressCode: Autoregressively Sewing and Generating Garments from TextGuidance
- 📍 2025 - AIpparel: A Multimodal Foundation Model for Digital Garments